Self-hosted Temporal Nexus
Temporal Nexus is now Generally Available. Learn why you should use Nexus in the evaluation guide.
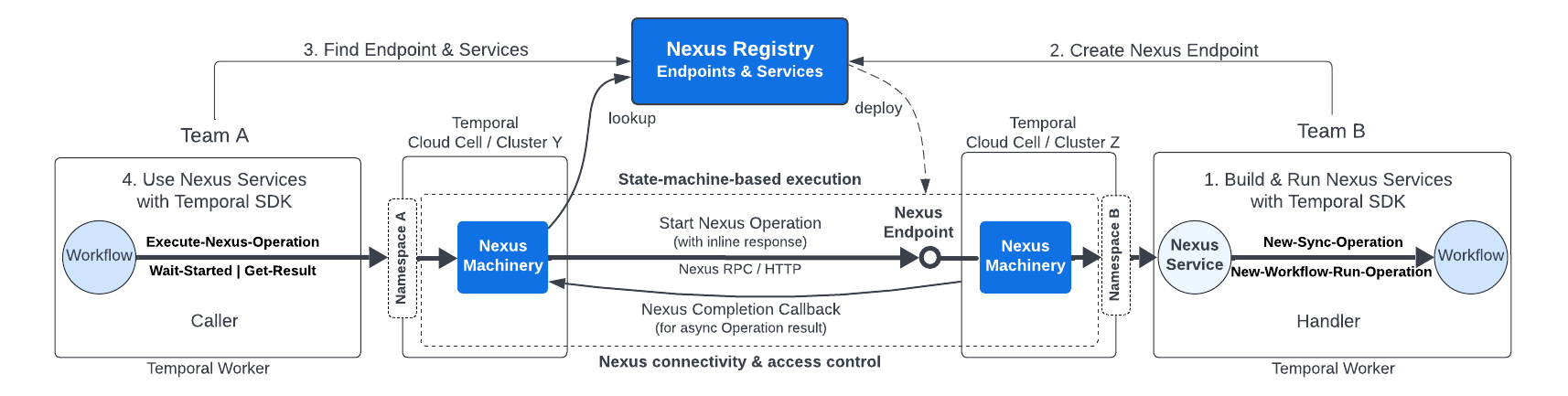
Temporal Nexus allows you to reliably connect Temporal Applications. It was designed with Durable Execution in mind and enables each team to have their own Namespace for improved modularity, security, debugging, and fault isolation.
Nexus Overview
Enable Nexus
Enable Nexus in your self-hosted Temporal Service by updating the server's static configuration file and enabling Nexus through dynamic config, then setting the public callback URL and allowed callback addresses. Nexus is only supported in single cluster setups at this time. For additional information on operating Nexus workloads in your self-hosted cluster, see Nexus Architecture.
Replace $PUBLIC_URL with a URL value that's accessible to external callers or internally within the cluster.
Currently, external Nexus calls are considered experimental so it should be safe to use the address of an internal load balancer for the Frontend Service.
To enable Nexus in your deployment:
-
Ensure that the server's static configuration file enables the HTTP API.
services:
frontend:
rpc:
# NOTE: keep other fields as they were
httpPort: 7243
clusterMetadata:
# NOTE: keep other fields as they were
clusterInformation:
active:
# NOTE: keep other fields as they were
httpAddress: $PUBLIC_URL:7243 -
Set the required dynamic configuration
-
Prior to version 1.30.X, you must enable Nexus through dynamic config, set the public callback URL, and set the allowed callback addresses.
NOTE: the callback endpoint template and allowed addresses should be set when using the experimental "external" endpoint targets.
system.enableNexus:
- value: true
component.nexusoperations.callback.endpoint.template:
# The URL must be publicly accessible if the callback is meant to be called by external services.
# When using Nexus for cross namespace calls, the URL's host is irrelevant as the address is resolved using
# membership. The URL is a Go template that interpolates the `NamepaceName` and `NamespaceID` variables.
- value: https://$PUBLIC_URL:7243/namespaces/{{.NamespaceName}}/nexus/callback
component.callbacks.allowedAddresses:
# Limits which callback URLs are accepted by the server.
# Wildcard patterns (*) and insecure (HTTP) callbacks are intended for development only.
# For production, restrict allowed hosts and set AllowInsecure to false
# whenever HTTPS/TLS is supported. Allowing HTTP increases MITM and data exposure risk.
- value:
- Pattern: "*" # Update to restrict allowed callers, e.g. "*.example.com"
AllowInsecure: true # In production, set to false and ensure traffic is HTTPS/TLS encrypted -
Since version 1.30.X, Nexus is enabled by default, the only configuration needed is to use the system callback URL.
component.nexusoperations.useSystemCallbackURL:
- value: true
-
Build and use Nexus Services
Nexus has a familiar programming model to build and use Nexus Services using the Temporal SDK. The Nexus Operation lifecycle supports both synchronous and asynchronous Operations. Nexus Operations can be implemented with Temporal primitives, like a Workflow, or execute arbitrary code.
Learn more
- Evaluate why you should use Nexus and watch the Nexus keynote and demo.
- Learn key Nexus concepts and how Nexus works in the Nexus deep dive talk
- Explore additional resources to learn more about Nexus.